Unlock the World of Crypto
Your guide to navigating the crypto landscape with confidence. Expert insights, investment strategies, and up-to-date information.

Crypto Addresses
Crypto addresses are alphanumeric strings that act as virtual locations for receiving and sending cryptocurrencies on a blockchain. Think of them like email addresses or bank account numbers, but for digital assets. Each address is unique and tied to a specific cryptocurrency network. They are essential for transacting in the crypto world, allowing you to securely send and receive funds.
Importance of Understanding Crypto Addresses
Understanding the structure and purpose of crypto addresses is crucial for avoiding errors and ensuring successful transactions. Always double-check the address before sending any crypto, as mistakes can lead to irreversible loss of funds. Different cryptocurrencies use different address formats, so it's important to verify that the address is compatible with the cryptocurrency you're sending.
Example of BTC Address
A Bitcoin address is a string of letters and numbers that identifies a destination on the Bitcoin network. They usually start with “1”, “3”, or “bc1” depending on the address type.
Here are a few examples of what they look like (these are just samples, not real wallets with funds):
Legacy (P2PKH, starts with 1): 1BoatSLRHtKNngkdXEeobR76b53LETtpyT
Pay-to-Script-Hash (P2SH, starts with 3): 3J98t1WpEZ73CNmQviecrnyiWrnqRhWNLy
Bech32 (SegWit, starts with bc1): bc1qar0srrr7xfkvy5l643lydnw9re59gtzzwf5mdq
👉 Each of these address types is valid, but they serve slightly different purposes and offer different levels of efficiency and fee savings.
👍 — here’s a clear breakdown of the three main types of Bitcoin addresses you’ll come across:
1. Legacy (P2PKH – Pay to Public Key Hash)
Format: Starts with “1” (e.g., 1BoatSLRHtKNngkdXEeobR76b53LETtpyT). Oldest type of Bitcoin address, introduced with the original Bitcoin system.
Compatibility: Supported by all wallets and exchanges.
Drawbacks: Higher transaction fees compared to newer address types because they use more block space.
2. P2SH (Pay to Script Hash)
Format: Starts with “3” (e.g., 3J98t1WpEZ73CNmQviecrnyiWrnqRhWNLy).
Allows more complex transactions, such as multisignature wallets or scripts.
Introduced as an upgrade to improve flexibility and make advanced features easier to use.
Compatibility: Widely supported, works on most wallets/exchanges. Fees: Slightly more efficient than legacy but not as good as Bech32.
3. Bech32 (SegWit)
Format: Starts with “bc1” (e.g.,
bc1qar0srrr7xfkvy5l643lydnw9re59gtzzwf5mdq).
Segregated Witness (SegWit) format, introduced to reduce transaction size and improve efficiency.
Benefits: Lowest transaction fees (uses less block space).
Fewer errors when copying/typing addresses (case-insensitive and error-detecting format).
Compatibility: Not all older wallets and exchanges support Bech32 yet, though support is becoming standard.
✅ Quick Summary: Legacy (1): Oldest, most compatible, but higher fees.
P2SH (3): Adds flexibility (scripts, multisig), widely supported.
Bech32 (bc1): Most modern, cheapest fees, but not always supported by outdated wallets/exchanges.
An Ethereum (ETH) address looks different from a Bitcoin address.
Format: Always starts with “0x” and is followed by 40 hexadecimal characters (numbers 0–9 and letters a–f).
Example (not real, just a sample): 0x32Be343B94f860124dC4fEe278FDCBD38C102D88
👉 Key things to know:
Ethereum addresses are case-insensitive (uppercase and lowercase don’t matter).
Sometimes you’ll see mixed-case addresses (like the example above). That’s called a checksummed address, which helps detect typos.
Unlike Bitcoin, Ethereum only uses this one standard address format for sending/receiving ETH and tokens (ERC-20, ERC-721 NFTs, etc.).
👍 — it’s super common for people to mix up Ethereum addresses and wallets, but they’re not the same thing. Here’s the breakdown:
An Ethereum address is like your bank account number.
It’s a unique identifier on the Ethereum blockchain that shows where funds (ETH or tokens) can be sent.
Example: 0x32Be343B94f860124dC4fEe278FDCBD38C102D88
Anyone can see the balance and transaction history of an Ethereum address on a block explorer (like Etherscan).
You can have multiple addresses inside a single wallet.
Ethereum Wallet
A wallet is more like your bank app — it’s the software or hardware that manages your Ethereum addresses and gives you access to your funds.
A wallet stores your private keys (secret codes that let you spend ETH/tokens from your address). Types of wallets:
Software wallets (e.g., MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Coinbase Wallet). Hardware wallets (e.g., Ledger, Trezor) for extra security.
Your wallet can generate and manage many Ethereum addresses for you.
✅ Simple analogy:
Address = your bank account number (public, for receiving money).
Wallet = your banking app (private, gives you control of accounts and transactions).
Understanding Cryptocurrency: A Beginner's Guide

What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized, digital ledger that records transactions across many computers. This makes it secure and transparent.
Key Crypto Terms
Learn essential cryptocurrency terminology like wallets, private keys, mining, and consensus mechanisms for better understanding.

Investing Basics
Start with small investments and research thoroughly before diving into the crypto market. Understand the risks involved.
Cryptocurrency Insights: Market Trends and Analysis
Analyzing Price Charts
Mastering price chart analysis to identify potential buying and selling opportunities in the volatile crypto market.

Emerging Technologies
Exploring new blockchain technologies and their potential impact on the future of cryptocurrency and finance.

Regulatory Landscape
Staying informed about cryptocurrency regulations worldwide to make compliant and informed investment decisions.
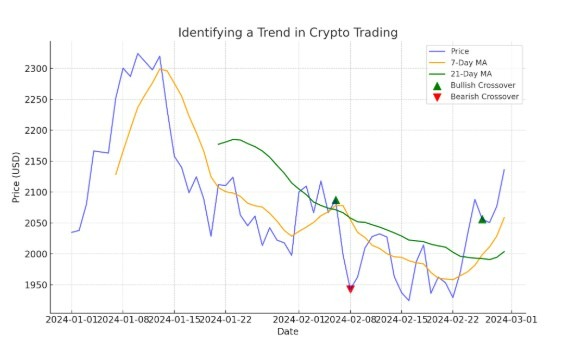
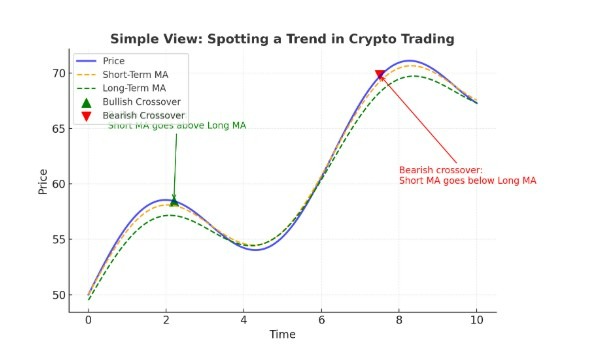
Here’s a chart showing how to spot trends in crypto trading using moving averages:
Blue line = Actual crypto price.
Orange line = Short-term trend (7-day moving average).
Green line = Long-term trend (21-day moving average).
Green arrows (▲) = Bullish crossover (short-term trend rises above long-term trend → possible uptrend).
Red arrows (▼) = Bearish crossover (short-term trend falls below long-term trend → possible downtrend).
How to identify the trend:
Uptrend – Price above both moving averages, and short MA above long MA.
Downtrend – Price below both moving averages, and short MA below long MA.
Trend change signals – Crossovers between short and long MAs often mark potential shifts in direction.
Simple View chart below
Blue line = Price movement.
Orange dashed line = Short-term moving average (reacts faster).
Green dashed line = Long-term moving average (reacts slower).
Green arrow (▲) = Bullish crossover → short-term trend moves above long-term → possible uptrend start.
Red arrow (▼) = Bearish crossover → short-term trend moves below long-term → possible downtrend start.
Crypto Currency Information: News, Updates, and Resources

Daily Crypto News
Get daily updates on the latest cryptocurrency news, market developments, and industry announcements.

Educational Resources
Access a comprehensive library of educational resources, including articles, guides, and tutorials on cryptocurrency.
Community Forums
Connect with other cryptocurrency enthusiasts in our online community forums to share insights and ask questions.
Our Services

Educational Resources
Extensive learning materials and workshops to deepen your understanding of cryptocurrency investing.

Investment Guidance
Personalized investment advice tailored to your risk tolerance and financial goals in the crypto market.

Portfolio Management
Expert management of your crypto portfolio to optimize returns and minimize risk.