Unlock the World of Crypto
Your guide to navigating the crypto landscape with confidence. Expert insights, investment strategies, and up-to-date information.

Understanding Cryptocurrency: A Beginner's Guide

What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized, digital ledger that records transactions across many computers. This makes it secure and transparent.
Key Crypto Terms
Learn essential cryptocurrency terminology like wallets, private keys, mining, and consensus mechanisms for better understanding.

Investing Basics
Start with small investments and research thoroughly before diving into the crypto market. Understand the risks involved.
What Is A Crypto Wallet
A crypto wallet is like a digital version of your real-life wallet — but instead of holding cash and cards, it stores the tools you need to access, send, and receive cryptocurrency.
Here’s the breakdown:
1. What it actually stores Not your coins directly — Your coins live on the blockchain (a public digital ledger). What the wallet holds is your private keys — secret codes that prove you own and can use your crypto. It also has public keys and wallet addresses — like your bank account number, which you can share to receive funds.
2. Two main types of wallets:
A. Hot wallets – connected to the internet Examples: mobile apps, web wallets, desktop software. Pros: Convenient, fast access. Cons: More vulnerable to hacking.
B. Cold wallets – offline storage Examples: hardware wallets (USB-like devices), paper wallets. Pros: Very secure against online attacks. Cons: Less convenient for frequent transactions.
3. How it works in practice:
Receiving crypto: Someone sends it to your wallet address.
Sending crypto:
You use your private key to sign a transaction, telling the blockchain, “Yes, I’m the rightful owner—move these coins.”
Security tip:
If you lose your private key (and have no backup), you lose access to your crypto permanently.
💡Simple analogy:
Blockchain = a giant public bank ledger.
Public address = your account number (you can share it).
Private key = your account PIN (keep it secret).
Wallet = your bank card that stores the PIN and lets you access the account.
What Is A Crypto Mining
Crypto mining is the process of using computers to help run and secure a cryptocurrency network — and getting rewarded with new coins for doing it. Let’s break it down simply:
Let's break it down:
Why mining exists: Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin run on a decentralized network (no bank or central authority).
The network needs people (miners) to:
Validate transactions – make sure no one is cheating.
Add transactions to the blockchain – the permanent public ledger.
Keep the network secure – by making it hard for bad actors to alter data.
2. How mining works (step-by-step)
1. Transactions happen — People send crypto from one wallet to another.
2. Miners gather transactions into a “block.”
3. Miners solve a puzzle — A very hard mathematical problem called a cryptographic hash.
This requires powerful computers doing millions of guesses per second.
This is called Proof of Work (PoW).
First miner to solve it gets to add the block to the blockchain.
Reward — That miner earns newly created coins plus transaction fees.
Types of mining:
ASIC mining – Specialized machines built just for mining.
GPU mining – Uses powerful graphics cards (common for altcoins).
CPU mining – Regular computer processors (mostly obsolete).
Cloud mining – Renting mining power from someone else’s hardware.
Challenges of mining:
High electricity use — Mining consumes a lot of power.
Expensive equipment — Good mining rigs aren’t cheap.
Competition — More miners = harder puzzles.
Not all coins are mineable — Some use other systems like Proof of Stake instead.
💡 Simple analogy:
Mining is like a giant math competition where thousands of people are racing to solve a puzzle. The winner gets the prize (new coins) and the right to write the next page of the blockchain “history book.”
Cryptocurrency Insights: Market Trends and Analysis
Analyzing Price Charts
Mastering price chart analysis to identify potential buying and selling opportunities in the volatile crypto market.

Emerging Technologies
Exploring new blockchain technologies and their potential impact on the future of cryptocurrency and finance.

Regulatory Landscape
Staying informed about cryptocurrency regulations worldwide to make compliant and informed investment decisions.
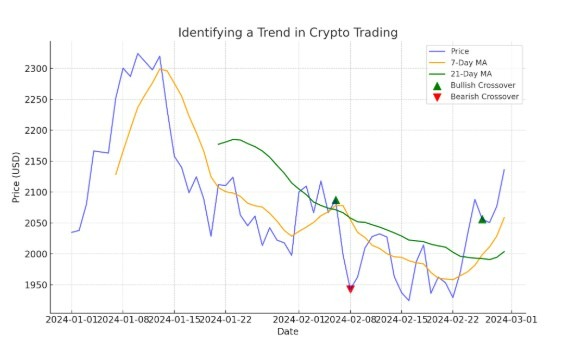
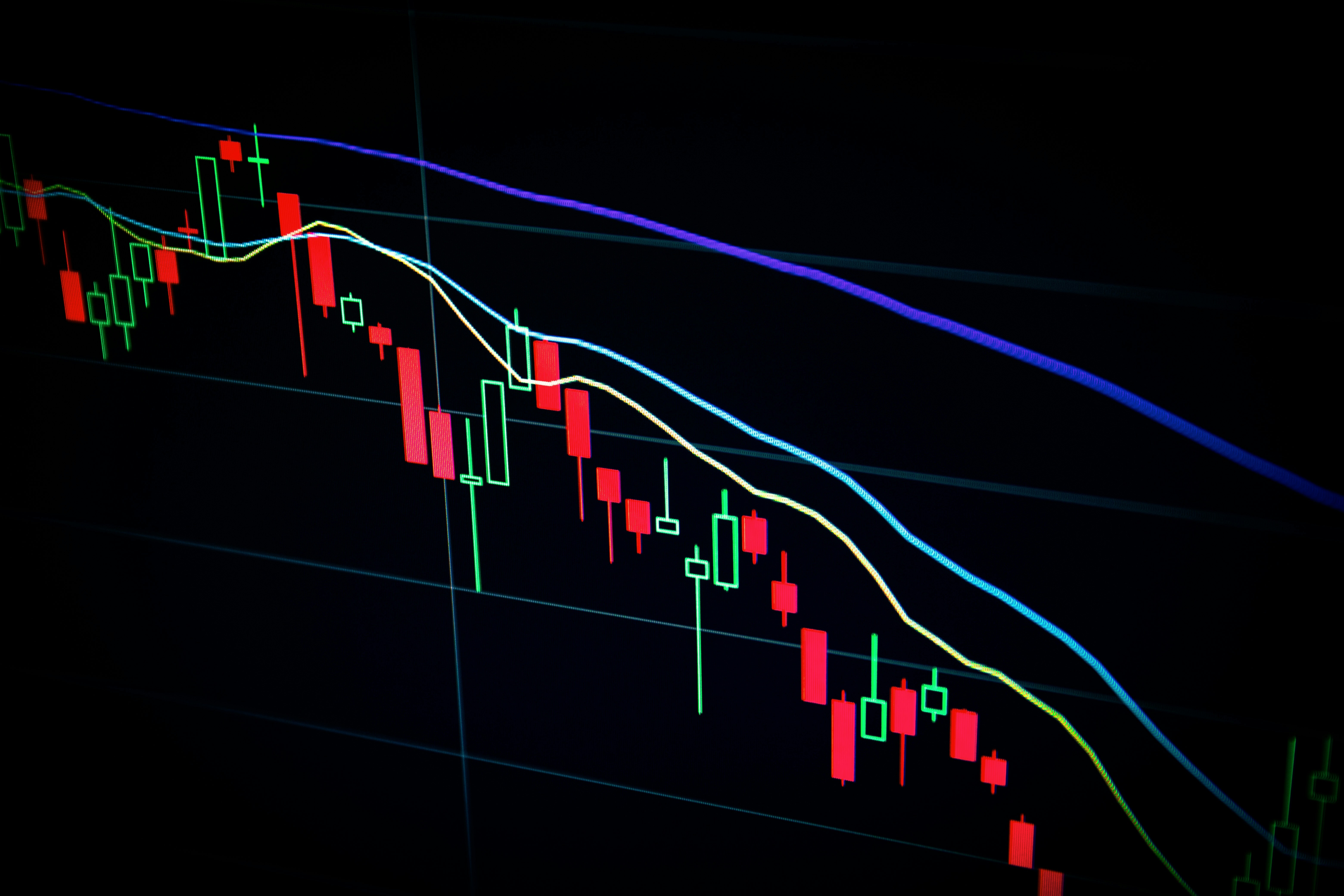
Here’s a chart showing how to spot trends in crypto trading using moving averages:
Blue line = Actual crypto price.
Orange line = Short-term trend (7-day moving average).
Green line = Long-term trend (21-day moving average).
Green arrows (▲) = Bullish crossover (short-term trend rises above long-term trend → possible uptrend).
Red arrows (▼) = Bearish crossover (short-term trend falls below long-term trend → possible downtrend).
How to identify the trend:
Uptrend – Price above both moving averages, and short MA above long MA.
Downtrend – Price below both moving averages, and short MA below long MA.
Trend change signals – Crossovers between short and long MAs often mark potential shifts in direction.
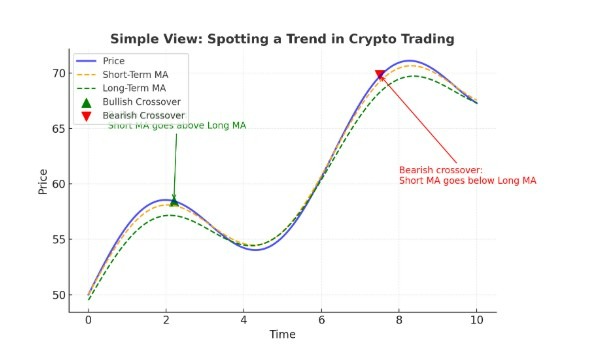
Simple View chart below
Blue line = Price movement.
Orange dashed line = Short-term moving average (reacts faster).
Green dashed line = Long-term moving average (reacts slower).
Green arrow (▲) = Bullish crossover → short-term trend moves above long-term → possible uptrend start.
Red arrow (▼) = Bearish crossover → short-term trend moves below long-term → possible downtrend start.
Crypto Currency Information: News, Updates, and Resources

Daily Crypto News
Get daily updates on the latest cryptocurrency news, market developments, and industry announcements.

Educational Resources
Access a comprehensive library of educational resources, including articles, guides, and tutorials on cryptocurrency.
Community Forums
Connect with other cryptocurrency enthusiasts in our online community forums to share insights and ask questions.
Our Services

Educational Resources
Extensive learning materials and workshops to deepen your understanding of cryptocurrency investing.

Investment Guidance
Personalized investment advice tailored to your risk tolerance and financial goals in the crypto market.

Portfolio Management
Expert management of your crypto portfolio to optimize returns and minimize risk.




What Our Clients Say

Wealthcreationco helped me understand crypto and make smart investments.
John Davis

The expert guidance from Wealthcreationco has been invaluable. Highly recommended!
Dolor Sit

I've gained so much confidence investing in crypto thanks to Wealthcreationco.
Dolor Sit